Unfortunately having Crohn’s disease means that you may be at risk of developing some complications. Below are some of the complications found in people with Crohn’s disease.
Intestinal strictures are essentially narrowings in the intestine which can make it difficult for food matter to pass through.
They can be mild or severe and in the most severe cases can lead to a complete blockage, meaning no food or fluid can pass through that part of your intestine. If this happens emergency surgery is needed.
Strictures happen when scar tissue builds in the wall of the large or small intestine. This scar tissue occurs as a result of long periods of inflammation followed by healing. The building up of scar tissue in the same place can then cause strictures. If there is also swollen (inflamed) tissue in the area it can contribute to the narrowing.
Symptoms of intestinal strictures include:
If the stricture causes a full or near blockage then food and liquid may not be able to pass through at all. In these cases you may experience:

Fistulas are a common complication of Crohn’s disease (approximately one third of people with Crohn’s disease will develop a fistula).
Fistulas are like tunnels which can form and connect either two different parts of the bowel together or the bowel to other organs - such as the bladder, vagina or skin. The most common site that fistula form is in the tissue surrounding the anus.
Fistulas occur when excessive inflammation causes ulcers to form. In time these can then develop into tunnels.
Small fistulas may not cause any symptoms but larger ones can become infected, causing complications. This can cause:

Intestinal bleeding, inability to absorb nutrients, diarrhoea and some surgery can all play a role in vitamin and mineral deficiencies in people with Crohn’s disease.
Read more about vitamin and mineral deficiencies.

Malnutrition in Crohn’s disease happens because someone isn’t getting enough of the nutrients they need. This can be due to not have a varied enough diet or because they are unable to absorb the nutrients in their food due to inflammation or surgery.
Symptoms of malnutrition include:
Pyoderma gangrenosum is a rare skin condition that causes painful ulcers. If the ulcers become large they can become infected, causing you to feel unwell and have a high temperature. It usually occurs on the legs, but can occur anywhere on the body.
It may be treated using steroids or immunosuppressants.

Osteoporosis is a weakening of your bones. It can be caused by not absorbing nutrients or through long-term use of steroid medication. The main symptom is bone fractures.

BAM can affect people with Crohn’s disease affecting the ileum or who have had surgery to their ileum. It can cause chronic diarrhoea.
In Crohn's disease BAM occurs when your ileum (the last part of your small intestines) is unable to absorb bile salt which is released by your body to digest food as it travels through your small intestine.
If you aren't able to absorb the bile salt then it moves into your colon. Your body then sends water to the colon and this causes diarrhoea.
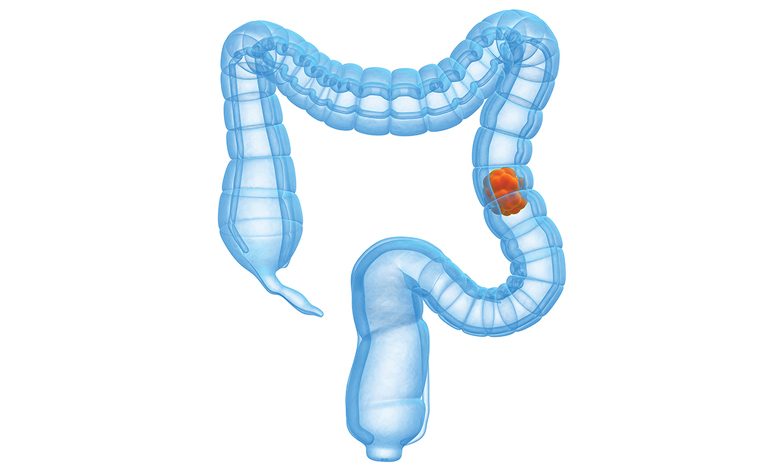
If you have Crohn’s disease affecting your colon you have a slightly increased risk of developing colorectal cancer. As a result you may be offered regular check-ups to look for colon cancer.
Other complications of Crohn’s disease include: