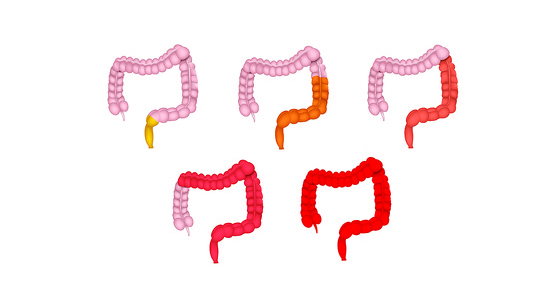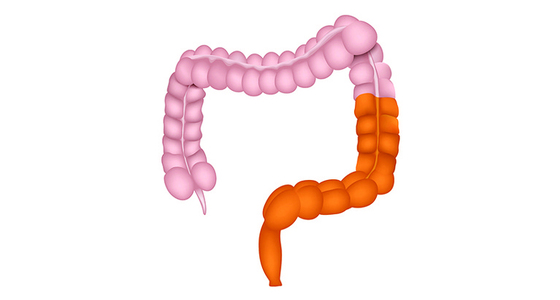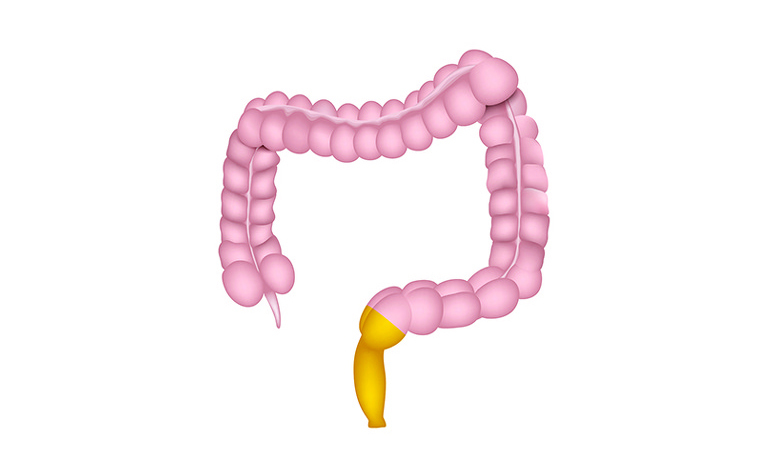
Ulcerative proctitis is a form of ulcerative colitis (UC) that affects only the rectum. It is often thought to be milder than other forms of UC, however it can develop into another type of UC over time.
It is a life-long chronic condition which cannot currently be cured and is part of a group of conditions known as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). UC causes inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract (gut).
In UC small ulcers develop on the colon’s lining which produce pus and mucus. This can cause abdominal discomfort and frequent emptying of the colon (diarrhoea). In ulcerative proctitis only the rectum is affected therefor the rest of the bowel can function normally.
Around 50% of people with UC are diagnosed with ulcerative proctitis or proctosigmoiditis.
Typical symptoms include:
Treatments currently include medication and surgery. Some people have severely inflamed or damaged parts of their colon surgically removed. This can reduce or eliminate the symptoms of ulcerative proctitis, however it does not get rid of the disease and there is a risk that it will return to another area of the colon in the future.
Some people also make adjustments to their diet and lifestyle to support their medical treatment - such as exercise, improving quality of sleep, reducing stress.

Serious complications are rare. Patients with only ulcerative proctitis probably do not have an increased risk of bowel cancer compared to the general population, whereas people with other forms of ulcerative colitis do have an increased risk.