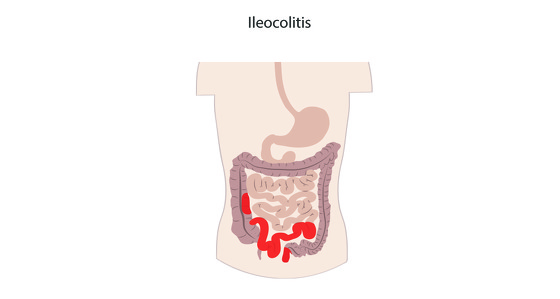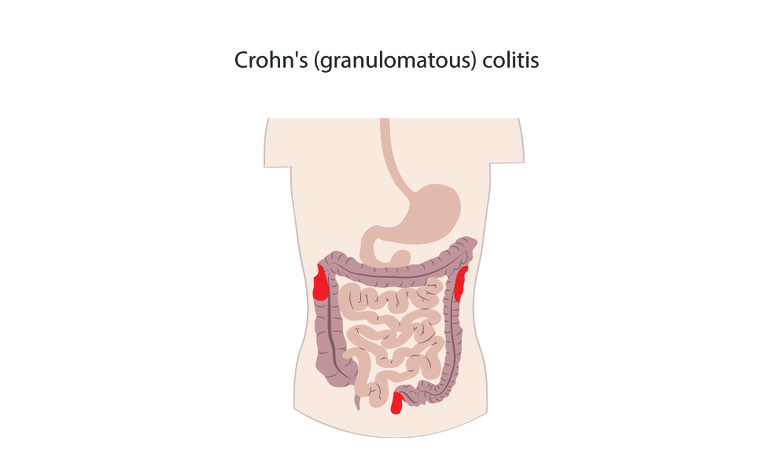
Granulomatous colitis, also known as Crohn's colitis, occurs only in the colon (also known as the large intestine or large bowel). It is often just known as Crohn’s colitis and is a form of Crohn’s disease. It accounts for around 20% of Crohn’s disease cases.
Crohn’s colitis is a lifelong chronic condition which cannot currently be cured and is part of a group of conditions known as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
When given a diagnosis of Crohn’s colitis some people believe they have both Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. However, this isn’t the case. Crohn’s colitis is a form of Crohn’s disease. The word 'colitis' simply means inflammation of the colon lining.
Due to inflammation in the colon in Crohn’s colitis bloody diarrhoea is a common symptom.
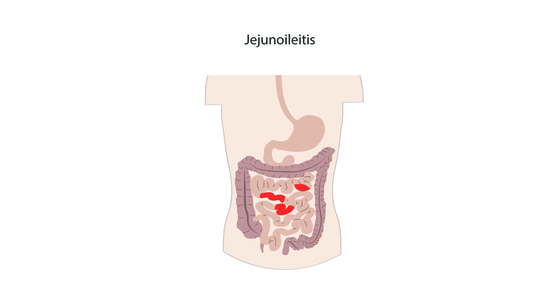
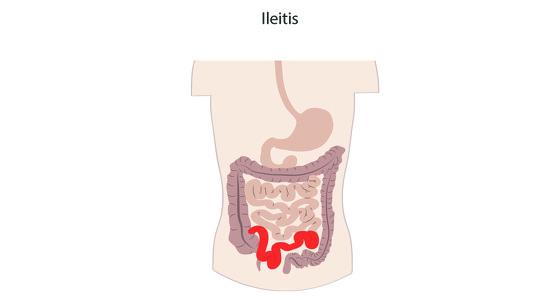
Crohn’s disease causes inflammation in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. It most commonly affects the small intestine and the beginning of the large intestine, however it can affect any part of the GI tract from the mouth to the anus.
Crohn’s disease can affect the entire thickness of the digestive tract wall and may also skip areas - meaning you could have inflammation near you mouth and also in your small bowel but no where in between.
It is common for people with Crohn’s disease to be diagnosed with more than one type of the condition if inflammation is present in several places in the GI tract.
Typical symptoms include:
Treatments currently include medication and surgery. Some people have severely inflamed or damaged parts of their bowels surgically removed. This can reduce or eliminate the symptoms, however it does not get rid of the disease and there is a risk that it will return to another area of the GI tract in the future.
Some people also make adjustments to their diet and lifestyle to support their medical treatment - such as exercise, improving quality of sleep, reducing stress.